Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Base Chemicals Functions
- Chemical Family
- Chemical Name
- Function
- Intermediate
- Technologies
- Product Families
- Chemical Structure
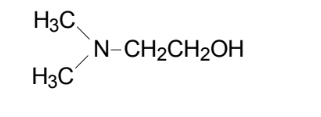
Applications & Uses
- Base Chemicals End Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Application Information
- Dimethylethanolamine is used in the preparation of water-reducible coating formulations. Government regulations covering the amount of organic solvent allowable in the air have spurred a search for emission control procedures. One of the most promising is the replacement of the organic solvent by water. The resins used in coating formulations are not water soluble but can be made so by reacting them with the amine.
- Dimethylethanolamine is one of the raw materials used to make dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate. Polymers produced from the methacrylate are useful as antistatic agents, soil conditioners, electrically conducting materials, paper auxiliaries, and flocculating agents
- Dimethylethanolamine can be used to control corrosion in boiler water condensate return lines. The dimethylethanolamine boils with the steam and is carried with it throughout the system. When the steam condenses, the dimethylethanolamine neutralizes any acidic components present in the condensate, thereby controlling the corrosion which would otherwise occur.
- Preparation of resins which can be used to increase the dry strength or wet strength of paper.
- Preparation of a good treatment which imparts water repellency and fungus resistance to kiln-dried lumber.
- Preparation of textile assistants.
- Improvement of polyalkene dyeability by mixing the polyalkene with a dimethylethanolamine-treated copolymer of ethylene and an acrylate or maleate.
- Preparation of catalysts for polymerizing olefin oxides and olefin sulfides.
- Stabilization of perchloroethylene by the addition of epichlorohydrin, propargyl alcohol, and dimethylethanolamine.
- Preparation of an antistatic agent for polystyrene.
- Preparation of a bonding agent for bonding thermoplastic organic polymers to conductive substrates.
- Preparation of ion-exchange resins.
- Evaporable wetting agent in glass cleaning formulation.
- Vapor phase catalyst for curing urethane-based ink.
- Esters form clear aqueous solutions on partial neutralization with mineral acid for use in cationic flow processes.
- Preparation of fatty acid soaps which are effective wax emulsifiers for water-resistant floor polishes, particularly polishes for light-coloredlinoleums.
- Used as an intermediate for the manufacture of antihistamines and local anesthetics in the pharmaceutical industry.
- Preparation of soluble chloromethylated polymers
- styrene and alpha-methyl styrene.
Properties
- Physical Form
- Soluble In
Regulatory & Compliance
Packaging & Availability
- Regional Availability
Storage & Handling
- Storage Information
- Storage Temperature: Dimethylethanolamine has an extremely low viscosity and freezing point (-73.5°F). It will not freeze or become viscous during normal handling even though subjected to very severe weather conditions.
- Dimethylethanolaminet should be stored under a dry inert gas blanket, such as nitrogen, to minimize contamination resulting from contact with air and water.
- Clean carbon steel is satisfactory as a material of construction for storage tanks and transfer systems, provided adequate precautions are observed to guard against rust contamination. In those cases where additional precautions are needed to preserve low color, stainless steel or aluminum should be used. Copper, or alloys containing copper, should be avoided.
Other
- Appearance
- Clear and substantially free of foreign matter
- Color (SDS)
- Clear Colorless
- Miscible in (SDS)
- Water
- Odor (SDS)
- Amine like
- Chemical Properties
Value Units Test Method / Conditions pH 10.0 - - Physical Properties
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Boiling Point 135.0 °C °C Density 0.89 g/mL g/mL Flash Point 41.0 °C °C Closed Cup Melting Point -59.0 °C °C Molecular Weight approx. 89.0 g/mol g/mol Viscosity 2.7 cSt cSt
