Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- RTU Product Type
- Technologies
- Product Families
Features & Benefits
- Ready-to-Use Product Features
- Features and Benefits
- Very high mechanical and electrical properties
- Very good thermal shock and crack resistance
- Excellent toughness combined with good dimensional stability
- High resistance to erosion under UV-radiation
- High tracking and arc resistance
Applications & Uses
- Application Area
- Composites Processing Methods
- Cure Method
- Product End Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Processing Information
The effective pot life is about 2 days at temperatures below 25°C. Dilute leftover mix at the end of a shift with the resin component prior to storage overnight or over the weekend and activate it with the other components just before restarting work. Piping containing prefilled components or casting mixes should be cooled immediately after work to prevent sedimentation and/or undesired viscosity increases. This helps minimize material losses and cleaning work. Viscosity increase and gel time at various temperatures, refer to Figs: 4.1 and 4.4.
Process Mold Temperature Demolding Time
(depending on mold temperature and casting volume)
Cure Conditions
(Postcure)
APG Process 130 - 150°C 10 - 30 min 5h at 140°C Conventional Vacuum Casting 80 - 100°C 2 - 4 h 8h at 140°C For any outdoor application, we recommend the use of silanised silica flour ; ex : Silbond W12-EST (Quarzwerke GmbH, Frechen, D)
To determine whether crosslinking has been carried to completion and the final proper- ties are optimal, it is necessary to carry out relevant measurements on the actual object or to measure the glass transition temperature. Different gelling and cure cycles in the manufacturing process could lead to a different crosslinking and glass transition temperature respectively.
Process Viscosities
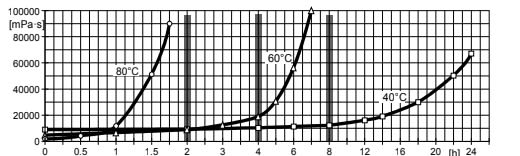
Fig.4.1: Viscosity increase at 40, 60 and 80°C(measurements with Rheomat 115) (Shear rate D = 10 s⁻¹)
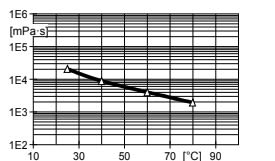
Fig.4.2: Initial viscosity as a function of temperature (measurements with Rheomat 115, D = 10 s⁻¹)
Gelation and Cure Time
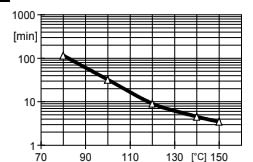
Fig.4.4: Geltime measured as a function oftemperature(measurements with Gelnorm Instrument ISO 9396)
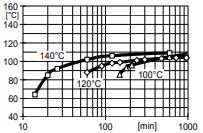
Fig.4.5: Glass transition temperature as a function of cure time (isothermio reaction, ISO 11357-2)
Mechanical and Physical Properties
Key Value Unit Test Method Condition Tensile strength 85 - 95 MPa ISO 527 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Elongation at break 1.5 - 2.0 % ISO 527 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
E modulus from tensile test 10,000 - 11,500 MPa ISO 527 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Flexural strength 145 - 165 MPa ISO 178 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Surface strain 1.5 - 2.0 % ISO 178 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
E modulus from flexural test 9,500 - 10,800 MPa ISO 178 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Compressive strength 185 - 195 MPa ISO 604 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Compression set 10 - 15 % ISO 604 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Impact strength 9 - 11 kJ/m² ISO 179-93 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Critical stress intensity factor (KIC) 2.6 - 2.9 MPa·m¹/² CG 216-0/89 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Specific energy at break (GIC) 600 - 750 J/m² CG 216-0/89 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Martens temperature 95 - 105 °C DIN 53458 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Glass transition temperature (DSC) 105 - 115 °C ISO 11357-2 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Coefficient of linear thermal expansion 35 - 37·10⁻⁶ K⁻¹ ISO 11359-2 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Thermal conductivity 0.85 - 0.95 W/mK ISO 8894-1 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Flammability (Thickness of specimen: 4 mm) Grade HB N/A UL 94 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Flammability (Thickness of specimen: 12 mm) Grade V0 N/A UL 94 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Water absorption (specimen: 50x50x4 mm) 0.10 - 0.15 % by wt ISO 62 10 days at 23°C, Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Water absorption (60 min at 100°C) 0.1 % ISO 62 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Decomposition temperature (heating rate: 10K/min) > 350 °C DTA Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Density (Filler load: 63 % by wt.) 1.7 - 1.8 g/cm³ ISO 1183 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Electrical Properties
Key Value Unit Test Method Condition Breakdown strength (3 mm plates) 18 - 22 kV/mm IEC 60243-1 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Breakdown strength (embedded Rogowski electrodes) 45 - 55 kV/mm Huntsman Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Diffusion breakdown strength Class HD 2 N/A DIN/VDE 0441-1 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Temperature of specimen after test 23 °C N/A Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
High Voltage arc resistance 189 - 192 sec IEC 61621 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Tracking resistance (with test solution A) CTI >600-0.0 N/A IEC 60112 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Tracking resistance (with test solution B) CTI >600M-0.0 N/A IEC 60112 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
High Voltage tracking resistance 2.5 kV IEC 60587-A Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Inclined Plane Tracking and Erosion Test (i.t.v.) 3.25 kV ASTM D 2303 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Time to track (t.t.t.) 2.5; >15 kV; h ASTM D 2303 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
Electrolytic corrosion A1 Grade IEC 60426 Determined on standard specimen at 23°C, Cured for 2h at 100°C + 16h at 140°C
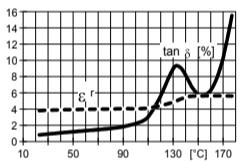
Fig.6.1: Loss factor (tan ) and dielectric constant ( r) as a function of temperature (measurement frequency: 50 Hz / IEC 60250/ DIN 53483)
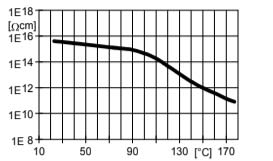
Fig.6.2: Volume resistivity ( ) as a function of temperature (measurement voltage: 1000 V/ IEC 60093/ DIN 53482)
Special Properties
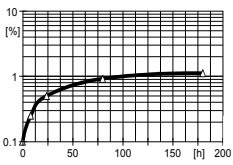
Fig.7.1: Water absorption at 100°C as a function of storage time (specimen : 50x50x4 mm, DIN 53495/1L)
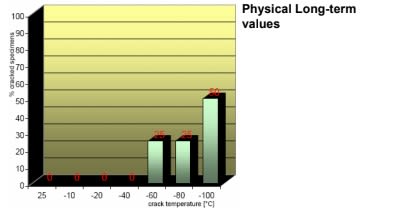
Fig.7.2: Crack resistance / Temperature shock test Passed specimen (%) as a function of temperature steps Average failure temperature: - 85°C Embedded metal parts with edge radius of 2 mm.
- Application Information
Outdoor electrical insulators for medium and high voltage in humid conditions, such as apparatus components, measuring transformers, bushings, etc.
- System Preparation
General instructions for preparing liquid resin systems.
- Long pot life is desirable in the processing of any casting resin system. Mix all of the components together very thoroughly at room temperature or slightly above and under vacuum. Intensive wetting of the filler is extremely important. Proper mixing will result in:
- Better flow properties and reduced tendency to shrinkage
- Lower internal stresses and therefore improved mechanical properties on object
- Improved partial discharge behaviour in high voltage applications.
- For the mixing of medium to high viscous casting resin systems and for mixing at lower temperatures, we recommend special thin film degassing mixers that may produce additional self-heating of 10-15°C as a result of friction. For low viscous casting resin systems, conventional anchor mixers are usually sufficient.
- In larger plants, two pre-mixers are used to mix the individual components with the respective quantities of fillers and additives under vacuum. Metering pumps then feed these premixes to the final mixer or a continuous mixer. The individual premixes can be stored at elevated temperature (about 60°C) for up to about 1 week, de-pending on formulation. Intermittent agitation during storage is advisable to prevent filler sedimentation.
- Mixing time can vary from 0.5 to 3 hours, depending on mixing temperature, quantity, mixing equipment and the particular application. The required vacuum is 0.5 to 8 mbar. Degassing time is recommended at least 1 hour. The vapour pressure of the individual components should be taken into account.
- In the case of dielectrically highly stressed parts, we recommend checking the quality consistency and pre-drying of the filler. Their moisture content should be <0.2%.
Properties
- Physical Form
Safety & Health
- First Aid Information
- Contamination of the eyes by resin, hardener or casting mix should be treated immediately by flushing with clean, running water for 10 to 15 minutes. A doctor should then be consulted.
- Material smeared or splashed on the skin should be dabbed off, and the contaminated area then washed and treated with a cleansing cream (see above). A doctor should be consulted in the event of severe irritation or burns. Contaminated clothing should be changed immediately.
- Anyone taken ill after inhaling vapours should be moved out of doors immediately.
- Handling Precautions
Protective clothing
Yes Gloves Essential Arm protector Recommended when skin contact likely
Goggestery diasses
Yes Respirator/dust mask
Recommended Skin protection before starting work
Apply barrier cream to exposed skin
Skin protection after washing
Apply barrier or nourishing cream
Skin protection cleansing of contaminated skin
Dab off with absorbent paper, wash with warm water and alkali-free soap, then dry with disposable towels. Do not use solvents
Clean shop requirements
Cover workbenches, etc. with light coloured paper. Use disposable breakers, etc.
Disposal of spillage
Soak up with sawdust or cotton waste and deposit in plastic-lined bin
Ventilation: of workshop
Renew air 3 to 5 times an hour
Ventilation: of workplace
Exhaust fans. Operatives should avoid inhaling vapours.
- Industrial Hygiene
Mandatory and recommended industrial hygiene procedures should be followed whenever our products are being handled and proccessed.
Other
- Application Information
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Mix Ratio 0.005 %(W) %(W) Accelerator : Resin Mix Ratio 3.1 %(W) %(W) Filler : Resin Mix Ratio 0.8 %(W) %(W) Hardener : Resin
